1black0white
We received this file of seemingly random numbers, but the person that sent it is adamant that it is a QR code. Can you figure it out for us?
We are given a file containing 29 lines of different numbers. Each line contains 9 numbers (except for 2 lines). From the title, we know we somehow need to convert the data we have been given into binary, which will represent a QR code in someway.
I first tried to convert each number into its binary representation:
qr_matrix = []
with open('qr_code.txt','r') as file:
for i, line in enumerate(file):
line = line.strip()
qr_matrix.append([])
for num in line:
qr_matrix[i].append(bin(int(num))[2:])
for row in qr_matrix:
for col in row:
print(col, end='')We can use this binary to QR Code converter, but the output isn’t a valid QR Code. The next idea was to treat each line as a number and do the same thing:
qr = []
with open('qr_code.txt','r') as file:
for line in file:
line = line.strip()
qr.append(bin(int(line))[2:])
for row in qr:
print(row, end='')This gave us something that resembled a QR Code, but it wasn’t able to be decoded properly. I used QRazyBox to force decode, and it was in flag format, just not the correct letters— so on the right track, but our conversion is wrong somewhere.
I then considered the idea that maybe we just need to plot the black and white pixels ourself, and not rely on a QR Code generator. I used some ANSI coloring magic to help print our “pixels”:
qr = []
with open("qr_code.txt", "r") as file:
for line in file:
line = line.strip()
line = int(line)
line = bin(line)[2:]
print(line)
qr.append(line)
scale_factor = 2
black = "\33[40m \33[0m"
white = "\33[47m \33[0m"
for row in qr:
print()
for col in row:
if col == "1":
print(black, end="")
else:
print(white, end="")This was printing something even more similar to a QR Code, but still not quite right.
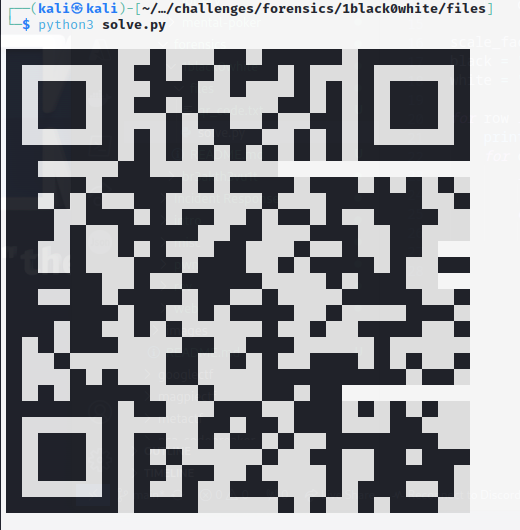
We are missing pixels still. Looking back at the text file, we are given 29 lines of numbers. Each line (except for the 2 mentioned previously) when converted to binary is 29 bits. All we need to do is pad the shorter numbers to 29 bits, and we should fill in the missing pixels.
padding = 29 # longest line is 29 bits
qr = []
with open("qr_code.txt", "r") as file:
for line in file:
line = line.strip()
line = int(line)
line = bin(line)[2:]
line = line.zfill(padding)
#print(line)
qr.append(line)
scale_factor = 2
black = "\33[40m \33[0m"
white = "\33[47m \33[0m"
for row in qr:
print()
for col in row:
if col == "1":
print(black, end="")
else:
print(white, end="")Running this script and decoding it gives us the flag:
`csawctf{1_d1dnt_kn0w_th1s_w0uld_w0rk}`